We all know that a good night's sleep is important, but have you ever wondered just how much deep sleep you actually need? It's not just about clocking in hours; it's about the quality of sleep, especially the deep kind that truly recharges you. Deep sleep is crucial for feeling rested, keeping your mind sharp, and maintaining your health. But here's the thing–not everyone needs the same amount of deep sleep. Age plays a crucial role in sleep patterns, which begs the question: how much deep sleep do you need for your age?
How much you need can change as you get older. Whether you're a busy parent, a hard-working professional, or enjoying retirement, understanding your deep sleep needs is key to waking up feeling refreshed and ready to chase your dreams and reach your goals. Let's explore how deep sleep varies with age and why it's so important for everyone.
What is Deep Sleep?
Sleep isn't just a single, uniform state that we slip into each night. It's a complex cycle made up of 4 different stages, each playing a unique role in our overall health. On a typical night, a person will go through four to six sleep cycles lasting, on average, 90 minutes each. Understanding these stages, especially deep sleep, is key to appreciating why we spend about a third of our lives asleep.
The Stages of Sleep
- Stage 1 (NREM N1): Lasting 1-7 minutes, this is the initial phase of sleep where you begin to drift off. It's a light sleep stage where you can be easily awakened.
- Stage 2 (NREM N2): Lasting 10-25 minutes, this stage involves further slowing down of brain activity. It's a period of light sleep before you enter deeper sleep.
- Stage 3 (NREM N3, also known as slow-wave sleep, delta sleep, or deep sleep): Lasting 20-40 minutes, this is the deep sleep stage. It's harder to wake someone up from this stage. During deep sleep, your body undergoes significant restorative processes.
- Stage 4 (REM Sleep): Lasting 10-60 minutes, this stage involves rapid eye movement and is known for vivid dreaming. Brain activity during REM sleep is similar to when you are awake.
The Importance and Benefits of Deep Sleep
Deep sleep, the N3 stage, is crucial for your physical and mental health:
- Physical Restoration: Deep sleep is essential for the body's repair process. It aids in healing and regeneration, supports immune function, and is crucial for growth and development.
- Mental and Cognitive Benefits: The deep sleep stage is vital for memory consolidation and learning. It helps in processing new information and retaining it.
- Emotional Well-being: Adequate deep sleep is linked to improved mood and emotional regulation. It plays a role in reducing stress and anxiety levels.
- Overall Health: Regular deep sleep can lower the risk of chronic health issues like heart disease, obesity, and diabetes.
Deep sleep is not just a passive state but an active and essential part of our daily cycle that supports various aspects of our physical and mental health. Understanding its role and ensuring we get enough of it is key to maintaining a healthy, balanced life.
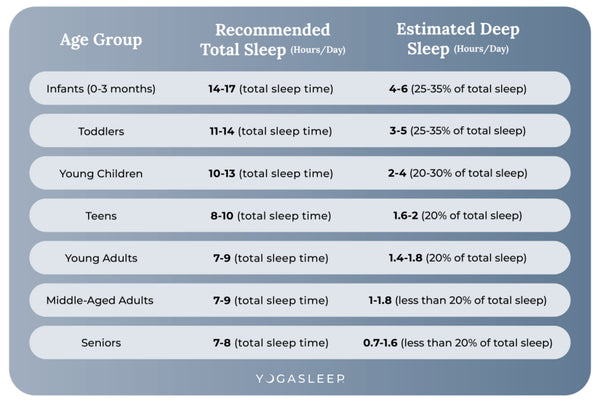
Deep Sleep Needs from Childhood to Old Age
Understanding the deep sleep requirements across different ages is crucial for maintaining health and well-being. Here's how deep sleep needs vary from infancy to old age:
Deep sleep needs change significantly from infancy to old age, reflecting the different developmental and physiological needs at each life stage. Gender may also impact the amount of deep sleep a person experiences during a typical night. Some evidence shows that men may be more prone to age-related decline in deep sleep than women. This knowledge can guide individuals in all age groups, from those wondering "how much deep sleep do I need?" to seniors curious about their sleep patterns, in understanding and optimizing their sleep for better health.
What Affects Your Deep Sleep?
Deep sleep is a crucial component of our overall health, but various factors can impact its quality and quantity. Understanding these can help in enhancing deep sleep.
Lifestyle Choices:- Diet and Nutrition: Consuming a balanced diet is essential for good sleep. Heavy or rich foods, spicy dishes, citrus fruits, and carbonated drinks can cause discomfort or heartburn, which may interrupt sleep. Caffeine and alcohol, especially when consumed late in the day, can also disrupt the sleep cycle.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can improve the quality of sleep, including deep sleep. However, exercising too close to bedtime may have a stimulating effect and hinder the ability to fall asleep.
- Sleep Environment: A comfortable, quiet, and dark sleep environment can promote better deep sleep. Factors like room temperature, mattress and pillow quality, and exposure to light and noise play significant roles.
- Stress: High levels of stress or anxiety can lead to sleep disturbances, including a reduction in deep sleep. The stress hormone cortisol can interfere with the sleep cycle.
- Mental Health Disorders: Conditions like depression, anxiety, and PTSD can negatively impact sleep patterns, often reducing the quality of deep sleep.
- Sleep Disorders: Disorders such as sleep apnea, insomnia, and restless legs syndrome can severely disrupt sleep architecture, reducing deep sleep.
- Chronic Illnesses: Health issues like diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and chronic pain conditions can affect sleep quality, including the amount of deep sleep.
- As people age, changes in sleep patterns are normal, often leading to a decrease in deep sleep. This change is attributed to alterations in the brain and other age-related health issues.
- Certain medications, including some antidepressants, high blood pressure medications, and stimulants, can affect sleep patterns. Substance abuse, particularly of alcohol and narcotics, can also severely impact deep sleep.
- Having a regular sleep schedule helps in maintaining a healthy sleep cycle. Irregular sleep patterns can disrupt the body's circadian rhythm and affect the quality of deep sleep.
Maximizing Deep Sleep at Any Age
Achieving quality deep sleep is crucial for health and well-being. Here are practical tips to enhance deep sleep across different age groups:
Creating a Sleep-Conducive Environment
- Optimize Your Bedroom: Ensure your bedroom is quiet, dark, and cool. Consider using blackout curtains or eye masks to block out light and distractions.
- Invest in Quality Bedding: A comfortable, cooling mattress and pillows can significantly improve sleep quality.
- Use Sound Machines: White noise or soothing sleep sounds can help deepen sleep quality. They mask distracting noises and create a calming sleep environment.
- Consider Sleep Trackers: These devices can provide insights into your sleep patterns, helping you make informed adjustments.
Establishing a Healthy Pre-Sleep Routine
- Stick to a Routine: Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends, to regulate your body's internal clock.
- Relaxation Techniques: Practices like meditation, deep breathing, or gentle yoga can help calm the mind and prepare the body for sleep.
- Limit Screen Time: Reduce exposure to screens at least an hour before bed to decrease blue light exposure, which can disrupt sleep.
Diet and Exercise for Better Sleep
- Mindful Eating: Avoid heavy meals, caffeine, and alcohol close to bedtime. Opt for light, sleep-promoting snacks if needed.
- Regular Physical Activity: Engage in regular exercise, but avoid vigorous workouts close to bedtime.
- Understand Sleep Patterns: Recognize and adapt to changes in sleep patterns as you age. For seniors, this might mean earlier bedtimes or wake times.
- Leveraging Sleep Technology
Health and Stress Management
- Manage Stress: Techniques such as mindfulness, journaling, or talking to a therapist can help manage stress, a common hindrance to deep sleep.
- Address Health Concerns: Regular check-ups can help identify and manage health issues that might affect sleep, such as sleep apnea or chronic pain.
Tailoring Deep Sleep for Every Age
It's clear that deep sleep is crucial for everyone, but how much we need changes as we age. From the significant needs of infants to the reduced requirements of seniors, recognizing the right amount of deep sleep is key to our overall health. Whether you're a young adult or moving into your later years, the question remains the same for many: how much deep sleep do I need, and how can I achieve it?
Creating a sleep-friendly environment is a practical step towards better sleep. Integrating soothing sleep sounds, for instance, can help deepen your sleep and ensure you get the rest you need. It's about making small changes that can lead to a big difference in your daily life and well-being.
Take Action for Better Sleep
Start by looking at your sleep habits. See what changes you can make, whether it’s tweaking your bedtime routine, using soothing sleep sounds to create a more relaxing environment, or just being more aware of your changing sleep needs as you age. Remember, good sleep is not just about quantity; it’s about quality, especially when it comes to deep sleep. Take the steps today for better sleep tonight and a healthier tomorrow.
https://troublesleeping.co.uk/age-and-sleep/ , https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6267703/ , https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5841578/
https://www.sleepfoundation.org/stages-of-sleep/deep-sleep








